Stress-strain Curve and Explain Different Phases of Curve
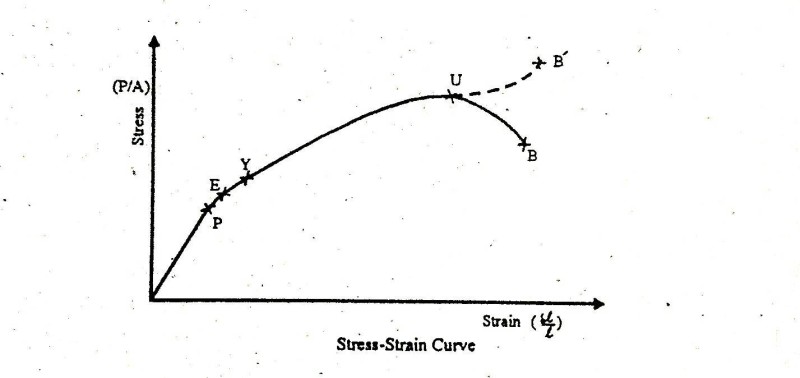
From the diagram one can see the different mark points on the curve. The stress-strain curve is a graph that shows the change in stress as strain increases.

Typical Stress Strain Curve For Destructive Tensile Testing Of Skeletal Download Scientific Diagram
Stress Strain Curve.

. Stress is represented along the Y-Axis. We observe the response of the material when stress is zero. Engineering stress-strain curves in which the original dimensions of the specimens are used in most calculations.
There are various points on a stress-strain curve that represent the strength of the material at different stages. Mathematically it is the amount of internal resistance force per unit area of the body. The stress-strain curve is a representation of the performance of the specimen as the applied load is increased monotonically usually to fracture.
It is a widely used reference graph for metals in material science and manufacturing. Point E represents the fracture point. Strain has no units.
In this diagram stresses are plotted along the vertical axis and as a result of these stresses corresponding strains are plotted along the horizontal axis. Stress-strain curves include an elastic stage oa elastic-plastic stage ab and post-failure stage and all samples can be divided into Brittle bc 1 Semi-Brittle bc 2 and Plastic bc. Stress strain curve is defined as the curve or a graphical representation of a materials stress and its strain and understood the relationship between stress and strain.
True stress and strain. Concrete is mostly used in compression that is why its compressive stress strain curve is of major interest. We all know that the three elements of force are magnitude direction and point of action.
It is produced by plotting concrete compress strain at various interval of concrete compressive loading stress. Stress strain curve is a behavior of material when it is subjected to load. Stress strain curve is a behavior of material when it is subjected to load.
There are various sections on the stress and strain curve that describe different behaviour of a ductile material depending on the amount of stress induced. Yield strength or yield stress is the material property defined as the stress at which a material begins to deform plastically whereas yield point is the point where nonlinear elastic plastic deformation begins. After plotting the stress and its corresponding strain on the graph we get a curve and this curve is called stress strain curve or stress strain diagram.
As shown below in the stress strain curve. Stress strain curve yield point is the material property defined as the stress at which a material begins to deform plastically. The area under the curve O to.
A Strainrefers to the measure of the deformation of the material because of the applied force. In this diagram stresses are plotted along the vertical axis and as a result of these stresses corresponding strains are plotted along the horizontal axis. The yield point is the point on a stress-strain curve that indicates the limit of elastic behavior and the beginning plastic behavior.
Once the yield point is passed some fraction of the deformation will be permanent and non-reversible. Point A is the elastic limit or proportional limit. Differences between Stress and Strain.
There are outstanding points and regions in such a curve corresponding to various stress and strain events. Prior to the yield point the material will deform elastically and will return to its original shape when the applied stress is removed. How to Draw Stress-Strain Curve or Diagram.
The stressstrain curves look different for compression and extension loadings. The stress-strain curve has different regions and points. In short it is the curve that is produced by plotting stress and strain values under different loads.
Here the strain is not permanent. Stress-strain curves are usually presented as. As shown below in the stress strain curve.
In this diagram stresses are plotted along the vertical axis and as a result of these stresses corresponding strains are plotted along the horizontal axis. Now the Stress-Strain curve is the graphical representation of the behavior of a material when the force is applied. Stress strain curve is a behaviour of material when it is subjected to load.
A tensile test is done on the material for drawing. Four Stages of the Stress-Strain Curve 1 Elastic region 2 Flow region 3 Strain hardening 4 Necking fracture Tensile Stress-Strain Curves for Materials with Different Properties What is Tensile Stress-Strain. The main reason is that the nominal stress is used where it is defined by the load divided by the specimen area where the area changes.
The curve based on the original cross-section and gauge length is called the engineering stress-strain curve while the curve based on the instantaneous cross-section area and length is called the true stress-strain curve. Point B is the elastic limit or upper yield point. As shown below in the stress strain curve.
This curve represent behavior of any material or object during loading condition. Yield Point and Yield Strength. When a metal is placed under.
The nominal strain is defined by the length change divided by the original length. If you observe a stress-strain curve you will notice that it is linear up to a point and then it is curved. It is stress to strain ratio.
In the region from. Point D represents ultimate strength. To plot this diagram stress is plotted along the vertical axis and strain is plotted on horizontal axis.
Strain is represented along the X-axis. Hookes law is obeyed. Stress is the internal resistance offered by the material or body when the external force is applied to it.
It is used to predict safe loading conditions failure point facture point etc. The stress-strain diagram for different material is different. The true stress and strains are defined as follows.
The force applied to object the object gets displaced that is stress and Strain is the change in the form or shape of the object or physical body on which stress is applied. The point OA in the graph represents the proportional limit. The different regions in the stress-strain diagram are.
On the stress-strain curve point E is the breaking stress point or Fracture point. From the diagram one can see the different mark points on the curve. In the region between O to A the curve is linear.
The fig is shown below. In this limit the stress-strain ratio gives us a proportionality constant known as Youngs modulus. It may vary due to the temperature and loading condition of the material.
Proportional limit point A Elastic limit point B Yield point upper yield point C and lower yield point D Ultimate stress point point E. If the load is increased further the strains increases rapidly. Point B is known as the elastic limit or yield point.
Here is the explanation of stress strain curve for mild steel which is ductile material. The first strain stage is elastic deformation. This diagram is very useful in design of any machine.
In the region A to B stress and strain and not proportional but body regains its original shape and size when the load is removed. Stress has units of force per area. I Proportional Limit It is the region in the stress-strain curve that obeys Hookes Law.
In this region the solid behaves as an elastic body. Stress strain curve of concrete is a graphical representation of concrete behavior under load. Here is the list of different stages when ductile material subjected to force till its failure.
Unless stated otherwise engineering stress-strain is generally used. Stress strain curve graph basic. Point C is the lower yield point.
Nm2 SI or lbin2 US Stress Resistive force F Unit Area A There are different types of stress as shown. In Stress strain Curve Strain is explained by when the force is applied to the object it gets into deformation It is measured to the deformation object to the original objectIt is the ratio of deformation to the original length. From the diagram one can see the different mark points on the curve.

Stress Strain Curve How To Read The Graph
Stress Strain Curve Explanation Stages Mild Steel Engineering Intro
Stress Strain And The Stress Strain Curve Materials Science Engineering
Three Stages Of The Stress Strain Curves A And The Stress Strain Download Scientific Diagram
Comments
Post a Comment